RC Time Calculator
RC Time Calculator
RL Time Calculator
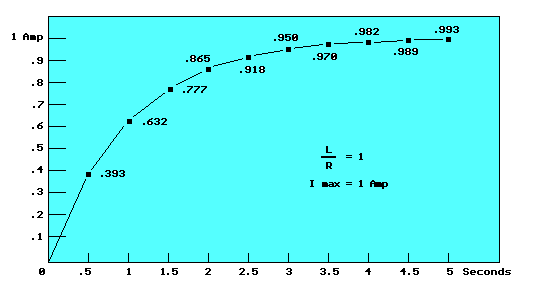
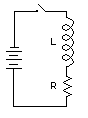 The drawing at the left illustrates an inductor with a series resistance and switch combination connected to a battery. The time required for the current to rise to 63.2% of the maximum value after the switch is closed is the ratio of inductance to resistance (L/R). The graph below illustrates the changing current of a 1 Henry inductor which has 1 ohm of resistance and is connected to a 1 volt battery. The current will increase from 0 to 632 milliamps in 1 second of time which is the ratio of inductance to resistance (L/R) = 1 second. The maximum value of current is determined from ohms law, or I=E/R = 1 volt / 1 Ohm = 1 amp. The calculator below can be used to determine various other points along the graph or the inductance and resistance needed for other situations. Four known values must be entered to solve for the unknown. For example, the instantaneous current of the
1 Henry/1 Ohm inductor below after 3.5 seconds of time is found by entering 1000 in the maximum current field, 1 in the resistance field, 1000 in the millihenrys field, and 3500 in the milliseconds field. Only one field should be blank or set to 0 before each calculation.
The drawing at the left illustrates an inductor with a series resistance and switch combination connected to a battery. The time required for the current to rise to 63.2% of the maximum value after the switch is closed is the ratio of inductance to resistance (L/R). The graph below illustrates the changing current of a 1 Henry inductor which has 1 ohm of resistance and is connected to a 1 volt battery. The current will increase from 0 to 632 milliamps in 1 second of time which is the ratio of inductance to resistance (L/R) = 1 second. The maximum value of current is determined from ohms law, or I=E/R = 1 volt / 1 Ohm = 1 amp. The calculator below can be used to determine various other points along the graph or the inductance and resistance needed for other situations. Four known values must be entered to solve for the unknown. For example, the instantaneous current of the
1 Henry/1 Ohm inductor below after 3.5 seconds of time is found by entering 1000 in the maximum current field, 1 in the resistance field, 1000 in the millihenrys field, and 3500 in the milliseconds field. Only one field should be blank or set to 0 before each calculation.Inductor Current With Respect To Time
Instantaneous Current = Maximum Current * ( 1 - e ^((-Time * R) / Inductance))